Data 360: What is Activation and Data Action?
Final Part
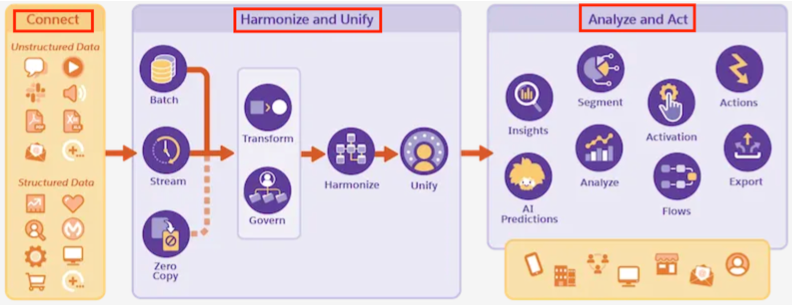
So far I have written about Connect, Harmonize and Unify. Then I wrote about Segmentation.
Now the final part of the process is to Act - Act using Activation.
Activation:
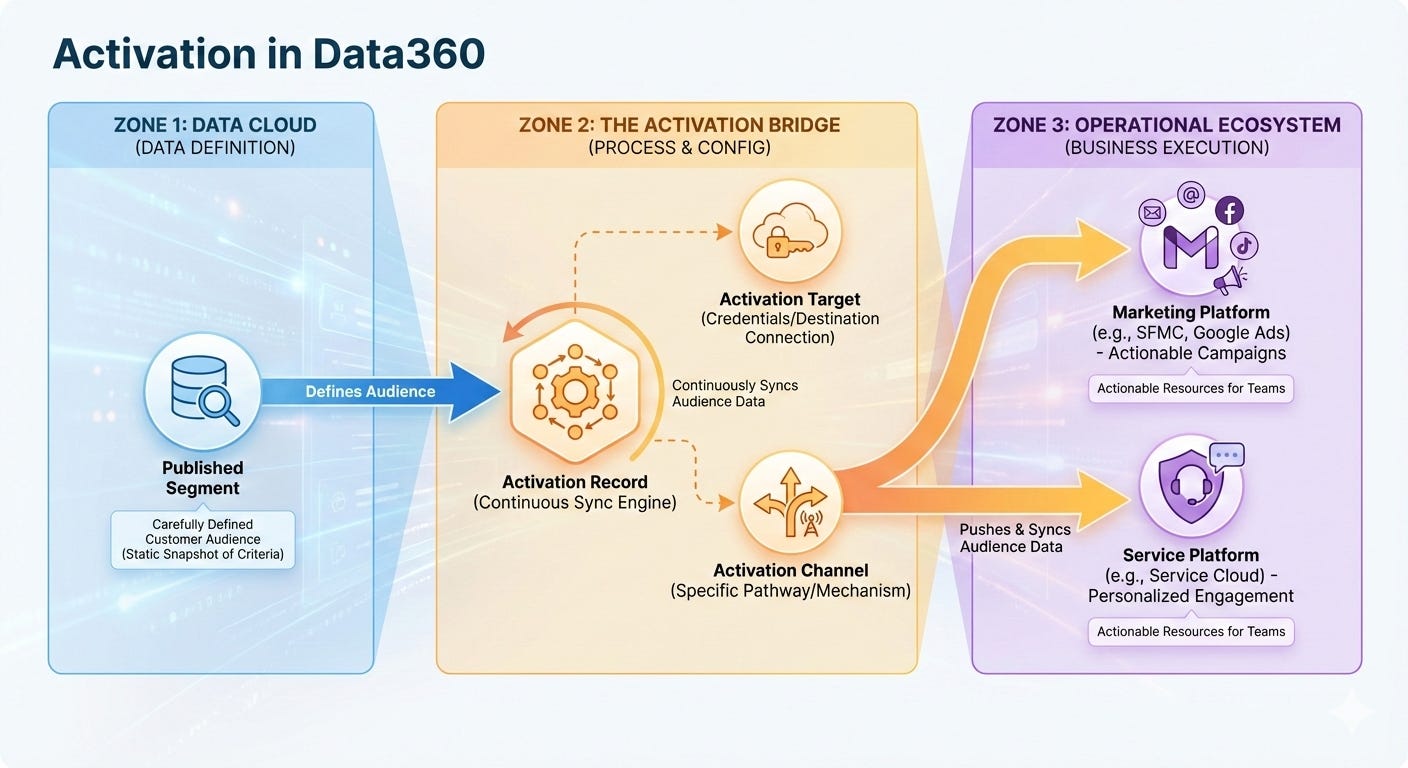
With Segmentation, we defined individuals to meet certain business criteria. But that is just the definition, how do we execute on them? How do we push them to tools like Marketing, Sales, Services so those tools can engage with these individuals?
Enters Activation. It takes the defined audiences through Activation Target (destination platform) and pushes relevant data to those platforms.
What are some of those destination platforms that Data 360 supports?
Marketing Cloud Engagement Activation
Creates a sendable Data Extension in your Salesforce Marketing Cloud Engagement instance. Required contact point: Email Address, Phone Number, or Mobile App. The segment data syncs to the Shared Data Extensions folder under “Customer 360 Segments,” where you can immediately reference it in email sends, SMS campaigns, and journey builder automations. This is the most common activation pattern for organizations with Salesforce marketing stacks.
File Storage Activation
Exports segment data and attributes to cloud storage: Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, or SFTP. The output is typically CSV, JSON, or Parquet format. This is ideal for data warehouse ingestion, analytics platforms, BI tools, or feeding data to downstream systems that aren’t directly connected to Salesforce.
B2C Commerce Activation
Syncs segments to Salesforce Commerce Cloud for real-time personalization on your e-commerce storefront. Example: Create a “VIP Customers” segment and activate it to Commerce Cloud so product recommendations and cart experiences are personalized for those customers.
External Platform Activation
Send segments to major ad platforms: Meta (Facebook), Google Ads, Amazon Ads, LinkedIn, and Google Display & Video 360. Data Cloud hashes and encrypts identifiers to match the platform’s audience specifications. Use case: Activate a “High-Intent B2B Leads” segment to Google Ads for remarketing campaigns.
In Summary, Activation has Three Core Elements
The Segment – The audience definition you created with specific filtering criteria (e.g., “customers who spent >$5,000 in last 12 months AND opened at least 5 emails”)
The Activation Target – The destination platform where segment data will be published (e.g., Marketing Cloud Engagement, Meta, file storage)
Personalization Attributes & Contact Points – The specific data fields included in the payload that reaches the activation target (e.g., email addresses, first names, customer ID, loyalty tier)
Let us look at few concrete examples
Example 1: E-Commerce Company – Email Campaign Activation
A retail company builds a segment: “Customers with 3+ purchases in past 6 months AND total spend >$500 AND haven’t purchased in last 30 days.”
• Activation Target: Marketing Cloud Engagement
• Contact Point: Email Address
• Attributes Included: First Name, Last Purchase Date, Lifetime Value, Favorite Product Category, Email Preference
• Output: Sendable Data Extension in SFMC named “WIN_BACK_VIP_CUSTOMERS”
• Use: Marketing Cloud Engagement marketer uses this DE in a journey builder automation to send a personalized “We Miss You” campaign with product recommendations based on purchase history.
Example 2: B2B SaaS – Ad Platform Activation
A SaaS company defines a segment: “Accounts with >10 logins per month AND used Feature X at least 5 times in last quarter.”
• Activation Target: Google Ads (external platform)
• Contact Point: Email Address (hashed for Google’s Audience Match)
• Attributes Included: Account Name, Industry, Company Size, Product Usage Score
• Output: Custom Audience in Google Ads
• Use: Sales team runs Google Search campaigns targeting these engaged accounts with messaging around advanced features and upsell opportunities.
Example 3: Financial Services – Data Warehouse Sync
A bank creates a segment: “Customers with account balance >$100K who haven’t accessed online banking in 60 days.”
• Activation Target: Amazon S3 (file storage)
• Contact Point: Customer ID, Email, Phone
• Attributes Included: Account Balance, Last Login Date, Product Holdings, Risk Profile, Preferred Channel
• Output: CSV file written to S3 bucket s3://data-lake/segments/inactive-high-net-worth/
• Use: Data warehouse team ingests the file into their analytics platform to analyze why these customers are disengaging, and service team uses the list for proactive outreach campaigns.
Example 4: Healthcare – Real-Time Personalization
A healthcare system activates a segment: “Patients with upcoming appointments in next 14 days.”
• Activation Target: Marketing Cloud Personalization (Interaction Studio)
• Contact Point: Email, Phone
• Attributes Included: Appointment Date, Provider Name, Facility Location, Insurance Plan, Clinical Notes (if applicable)
• Output: Real-time attribute sync to Interaction Studio
• Use: When patients visit the healthcare organization’s portal or app, Interaction Studio personalizes their experience—showing appointment details, pre-visit forms, parking instructions—based on their segment membership and attributes.
Example 5: Churn Prevention – Multi-Channel Journey
A SaaS company segments: “Customers who decreased login frequency by 50% in last 30 days AND opened a support case in last 14 days.”
• Activation Target: Marketing Cloud Engagement + Internal Salesforce CRM
• Contact Points: Email, Phone
• Attributes: Churn Risk Score, Last Login Date, Support Issue Category, Product Usage Trend
• Use Cases:
• Marketing: Triggered email offering help resources or special discounts
• Sales: Assigned to CSM for proactive check-in call
• Service: Support team alerted to priority status
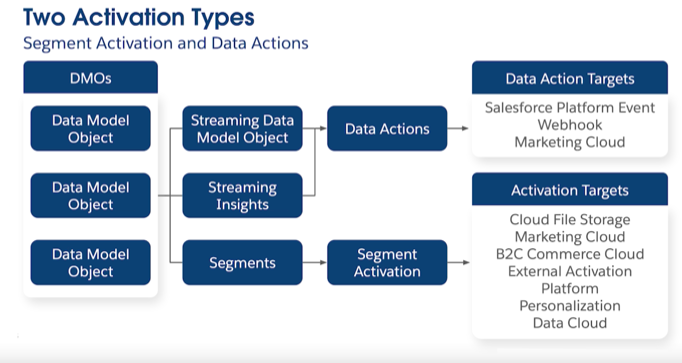
It is also necessary to understand 2 Types of Activation.:
Data Action (Real-time or near real-time)
Segment Activation (Scheduled or batch-based)
Data Action:
Data Action is a process that triggers an alert or event in real-time based on streaming data or calculated insights, sending that event to a target system to initiate an automation or integration.
Data Scope: Single event per trigger. When a condition is met, one event fires—not an entire audience sent at once.
Example: A customer browsing an e-commerce site adds a $200 item to cart. 60 minutes pass without checkout. A real-time data action detects “Cart > $100 AND time since add > 60 minutes.” Within 2 seconds, a data action fires to Marketing Cloud Engagement, which triggers a transactional email journey with “You left items in your cart” messaging. Customer receives email within minutes.
Segment Activation:
Segment Activation is simply “batch export of your audience.” It is the process of publishing a pre-defined segment to an activation platform, sending all matching records with their selected attributes to an external system on a scheduled basis.
Example: All the examples listed above apply to Segment activation. Like A retailer wants to send a “Black Friday VIP Sale” email to their highest-value customers, A financial services company wants to export all high-net-worth customer data to their data warehouse for advanced analytics.
With this I conclude the Data Cloud Series. One thing I didn't talk about is Calculated and Streaming Insights. I may write about it, if the inspiration strikes.

The realtime data action vs batch activation distinction is critical but often glossed over. Ive seen teams try to use segment activation for abandoned cart scenarios and wonder why conversions tanked the delay ruins the experiance. Data actions solve this but only if your streaming infra can handle the write throughput without bottlenecking at scale.